CYBERCRIME
Cybercrime is criminal activity that either targets or uses a computer, a computer network or a networked device. Most, but not all, cybercrime is committed by cybercriminals or hackers who want to make money. Cybercrime is carried out by individuals or organizations.
HISTORY OF CYBERCRIME
Cyber crime really began to take off in the early 2,000’s when social media came to life. The surge of people putting all the information they could into a profile database created a flood of personal information and the rise of ID theft.
TYPES OF CYBERCRIMES
- Phishing Scams
Phishing is a method of obtaining confidential or personal information from a computer user by a cybercriminal or hacker. This is mainly done by phishing websites, which are built to look just like a legitimate website in the hopes of tricking an unsuspecting computer user into entering personal information such as banking passwords. A person’s home address or even a person’s social security number We suggest using a phishing filter feature on your web browser to regularly search websites you visit to see if they have been detected as a phishing website to avoid phishing scams. - Identity Theft Scams Cybercriminals with access to your credit card or banking account details can make transactions in your name. Identity theft was a serious problem even before the Internet was invented, but as you might know, the virtual world has made it much easier for criminals to use and steal your identity. Closely monitoring your accounts is one of the simplest and least costly ways to protect your identity. If you see anything unusual, report it right away to the appropriate authorities. Avoid wasting time in these cases by being proactive. Identity theft scams are common on the internet, and they can take the form of a spam email, a website, or even a pop-up poll.
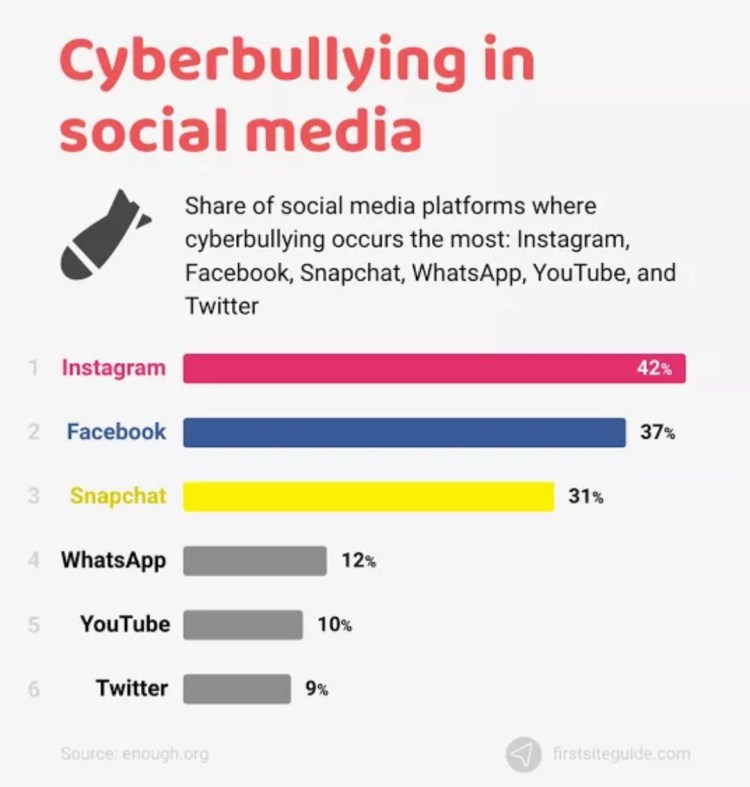
- Online Harassment Harassment on the internet is normally linked to your social life and whether or not you use a popular social media platform like Facebook or Twitter. Threats sent via email, text message, or social media message/post are examples of online harassment. It’s usually easy to report these threats to the social media platform where you’re being abused. Harassment can also lead to children being harassed online, which can have serious implications, as you might have seen recently in the news when a 13-year-old girl named Megan Meier from Dardenne Prairie, Missouri, committed suicide as a result of being bullied online. Even if you know the individual on the other end, our advice for dealing with online abuse is to report any unusual behavior right away before it gets out of control. Impostors who stalk you online always do so in order to reach your ‘breaking point,’ but you should never let it get that far.
- Cybertalking Cyberstalkers can go to any extent to keep track of a victim’s online activities. Infecting a person’s computer with malware capable of logging computer activity is one example. Cyberstalkers are also notorious for harassing their potential victims on a regular basis. Cases of cyberstalking, like cases of online abuse, should be reported to authorities. Cyberstalkers can contact a victim’s coworkers, acquaintances, and other online contacts in order to smear them or obtain personal information.
- Invasion of privacy Invasion of privacy is defined as someone trying to pry into another person’s personal life. Hacking into a person’s machine, reading their emails, and tracking their online activities are all examples of this. Many of these specific crimes are legally punishable. You can simply contact the police and file a report if you suspect someone is invading your privacy. Most of the time, local agencies can manage these cases without the assistance of an online law enforcement agency.
HOW TO PREVENT CYBERCRIME
1.Use a full-service internet security suite
For example, Norton Security protects you against current and emerging malware, such as ransomware and viruses, in real time, and helps protect your personal and financial details when you go online.
2.Use strong passwords Don’t use the same password on several sites, and change your passwords on a regular basis. Make them more complicated. This necessitates the use of at least ten letters, numbers, and symbols. A password management program can assist you in keeping your passwords safe.
3.Keep your software updated This is particularly critical when it comes to your operating system and internet security applications. To gain access to your device, cybercriminals often use known exploits, or vulnerabilities, in your software. Patching those exploits and flaws can make it less likely that you’ll become a cybercrime target.
4.Manage your social media settings Keep your personal and confidential information safe. With only a few data points, social engineering cybercriminals can also obtain your personal information, so the less you post publicly, the better. If you post your pet’s name or your mother’s maiden name, for example, you risk revealing the answers to two popular security questions.
5.Make your home network stronger
All traffic leaving your devices is encrypted before it reaches its destination, thanks to a VPN. If cybercriminals manage to break through your communication line, they will only be able to read encrypted data. When using a public Wi-Fi network, whether in a library, café, hotel, or airport, it’s a good idea to use a VPN.
6.Talk to your children about the internet You don’t have to close down communication networks to inform your children about appropriate internet use. Make sure they understand that they can come to you if they are being harassed, stalked, or bullied online.